A METHOD AND KIT FOR IDENTIFYING STROKE ETIOLOGY AND DETERMINING SECONDARY PREVENTION STRATEGIES (#2019008)
Ze’ev Itsekson-Hayosh ,Efrat Shavit-Stein, David Orion and Joab Chapman
Contact Us for more information:Tel Hashomer Medical Research, Infrastructure and Services Ltd.Innovation.office@sheba.health.gov.il |
| Categories | Stroke, diagnosis, treatment, classification |
| Development Stage | Clinical stage, first prototype |
| Patent Status | pending |
Background
Ischemic stroke is the 3rd leading cause of mortality in adults' worldwide and 1st leading cause of disability in adults. The mainstay of ischemic stroke management is focused on correct secondary prevention, based on stroke etiology.
The usual etiologic factors are shared by all cardiovascular diseases, such as smoking, dyslipidemia, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus and hypertension – which account for almost 40 percent of stroke cases, regardless the size of the occluded artery (whether by a mechanism of in-situ thrombosis or artery-to-artery embolism). Another 60% percent account for various probable other embolic causes, atrial fibrillation being the most common. However, in about 50% of presumed embolic stroke cases – the etiology remains unknown, despite repeated heart rhythm monitoring, cardiological and thrombophilia workup. Meaning that in one third of cases the cause of stroke remains unknown, terming those cases as cryptogenic.
Etiological origin of the thrombosis, has paramount importance in decision making process when choosing antithrombotic therapy for secondary prevention of ischemic stroke. Antiplatelet therapy being the most effective proven therapy only in causes of atherosclerosis (lacunar, artery-to-artery, large vessel in situ thrombosis or aortic arch plaque source). Anticoagulation pathways inhibition it reserved only for proven causes of thrombophilia or cardio-embolic causes, with new oral anticoagulants (NOACs) being approved only for cases of established atrial fibrillation. Thus rendering a tremendous amount of cryptogenic cases to potentially inefficient treatment.
The Need
Stroke endovascular procedure is a new effective treatment for large vessel occlusion and the number of patients treated is increasing rapidly since its introduction in 2008, with potential eligibility of nearly over 1 million new patients every year worldwide. Yet, after the thrombectomy is done and the thrombus (clot) is retrieved - in almost 35% of cases source of the thrombus remains unknown
Identifying the origin of the brain's clot is essential for clinical decisions on antithrombotic therapy following stroke. Currently, the etiological workup is lengthy, expensive, includes vascular imaging, cardiac echo, recurrent heart rhythm monitoring and laboratory tests for hypercoagulable states, and has a frustratingly low yield.
We suggest a novel diagnostic tool which will enable a fast (within 2 hours) and reliable method to elucidate the origin of the thrombus, thus allowing a tailored and adequate antithrombotic treatment.
Thrombin is the major coagulation factor which generates the thrombus by cleaving fibrinogen. Active thrombin is a constituent of many thrombi and its activity can be measured by a specific and unique fluorescence assay that we developed in our lab. We have found that thrombi retrieved from brain arteries differ in the temporal pattern of thrombin activity. With cardio-embolic thrombi secondary to atrial fibrillation having a clear distinctive pattern which may be used as a diagnostic marker.
The Technology and Innovation
According to the data collected and analyzed so far by our group (~60 patients) – there is a statistically significant difference of thrombin activity peak time between proven atrial fibrillation group versus the proven atherosclerosis group. While in most of the cryptogenic group – the thrombin-like clot peak activity is statistically similar to atrial fibrillation group
We have developed a rapid diagnostic tool by analysis of secreted thrombin activity from a clot freshly retrieved by endovascular thrombectomy procedure in acute stroke patients.
- We have generated and validated biochemical standards according to clot source.
- Our assay is an automatized kit that will allow rapid and validated clot source determination.
Advantages
Currently there is no known reliable and rapid method of retrieved acute ischemic stroke clots analysis in terms of biochemical activity and its correlation to stroke etiology, nor there is an alternative biochemically measurable marker. According to current American Heart Association guidelines – the only approved alternatives today are cardiac noninvasive analyses which have low sensitivity and cerebral angiography analysis which has low specificity. Existing laboratory trials – offer only a morphological analysis which is time consuming and does not allow a specific differentiation of atrial fibrillation causes.
The Product
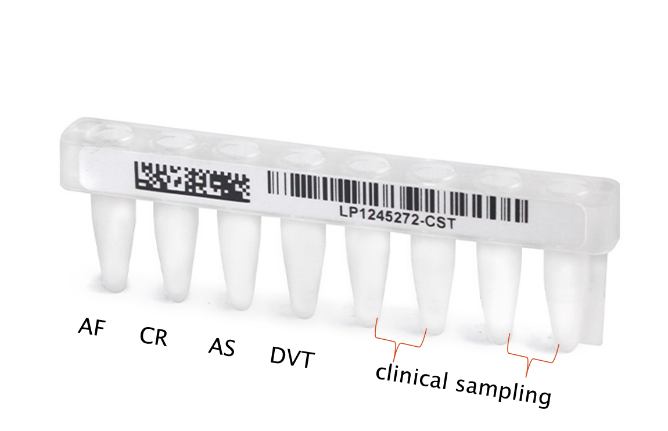
In-vitro Diagnostic Assay within disposable Plates or stipes or tubes with any configurations suitable for any reader containing the following biochemical:
- Validated thrombin values for :
AF-Atrial fibrillation,
CR-Cryptogenic (unknown)
AS-Atherosclerosis
AL-Acute leg ischemia
Duplicate for samples
2. Thrombin assay reagent
Potential Applications
- Correct and rapid stroke source diagnosis – based on validated standard values of ischemic stroke patients.
- Correlation of stroke severity to clot profile
- Clot data "bank" for future research.
The Market
- The global acute ischemic stroke diagnosis and treatment market to reach nearly US$ 2 Billion by 2023, at a CAGR of 5.3% over the forecast period, considering high incidence and prevalence of strokes.
- The Global Stroke Management Market accounted for $22.6 Billion in 2016, and is estimated to reach $36.8 Billion by 2023, growing at a CAGR of 7.1% during the analysis period (2017-2023).
- ~ 15 million people suffer a stroke worldwide each year
Of these, 5 million die and another 5 million are permanently disabled. - Approximately 60–80% of all strokes is ischemic .
- Around 40% of ischemic strokes are caused by a large artery occlusion and the patients must undergo a Thrombectomy
The major players in the global stroke diagnostics and therapeutics market comprise Medtronic plc, Abbott Laboratories, Cordis Corporation, Boston Scientific Corporation, GE Healthcare, Koninklijke Philips N.V., Stryker Corporation, Siemens AG, Merck & Co., Inc., and Genentech, Inc.
Contact Us for more information:Tel Hashomer Medical Research, Infrastructure and Services Ltd.Innovation.office@sheba.health.gov.il |



